| Workshop on Automatic Speech Annotation and Analysis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
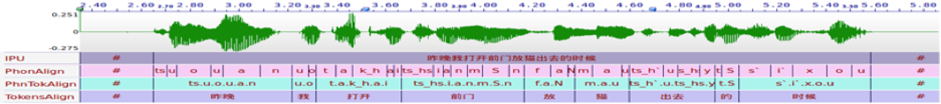
It has become more and more expected for linguists of different branches to take into account large quantities of empirical data, often including hours of recorded speech data, in formulating any linguistic theories. The biggest obstacle linguists are faced with today is not the availability of data, but its annotation and analysis. Though a number of tools have been developed in recent years to automate those labor-intensive tasks, most of them require a certain level of expertise in computer science, which is beyond the reach of most linguists without the help of an engineer. The aim of the four-day workshop is to introduce to linguists the principles and tools available to perform automatic speech annotation and analysis. It will provide hands-on practice on installing and using the following tools designed for linguists to do speech analysis: SPPAS – Automatic Annotation of Speech - an annotation software that allows users to create automatically, visualize and search annotations for audio data. Among others, it is able to produce automatic annotations of various linguistic domains including utterance, word, syllable and phonemes from a speech recording and its transcription. SPPAS is multi-lingual which is currently implemented for French, English, Italian, Spanish, Catalan, Polish, Mandarin, Japanese, Taiwan Southern Min and Cantonese. It is multi-platform (Linux, Windows, and MacOS), and is open source software issued under the GNU Public License. In addition to phonetic segmentation and alignment, word segmentation for spoken Cantonese will also be introduced. Momel – an algorithm for the automatic factoring of fundamental frequency contours into two components: a macromelodic component and a micromelodic component. INTSINT – a prosodic equivalent of the International Phonetic Alphabet. Originally designed as a descriptive tool for linguistic annotation, INTSINT has since been implemented as an algorithm converting the output of the Momel algorithm to a sequence of discrete tonal symbols which can then be used as input to synthesise a fundamental frequency contour. ProZed – a tool to test prosodic models of rhythm and melody using an analysis by synthesis paradigm to derive a synthetic output from an abstract representation of the prosody.
REGISTRATION Please send your full name, email address, institution, and the programme you are studying in your institution to the following email address: asaa.workshop@gmail.com Due to limited quota available, registration will be processed on a first-come-first-served basis. ENQUIRY Please contact Dr. Roxana Fung (roxana.fung@polyu.edu.hk). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

